Air Ionizers Are Potentially Hazardous to Your Health

Ionizers
Air Ionizers are mostly used in the air purification systems like an air-conditioning unit, refrigerators and even laptops. They ionize the air by electrically charging the air molecules – ionizing the atoms in the molecules. They negatively ionize the air and the negative ions by virtue attract the positively charged particles in the air, like bacteria, allergens, and other dust particle. They finally bond with the molecules, add up weight, and eventually fall down and stick to the ground or any furniture inside the room. This reduces the airborne particles and helps prevent any dust or bacteria getting into our respiratory system.
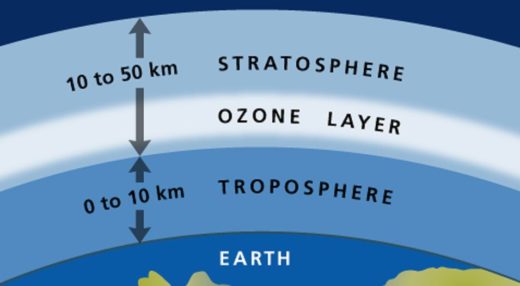
Ozone and Air Ionizers
Though the ionizers produce negative ions, which thereby help in maintaining a dust free ambiance, they also produce a harmful byproduct. As the air is ionized, the area next to the ionization chamber, usually of high voltage, breaks down the oxygen bond in the air. This leads to the formation of O3 (Ozone) when the free radicals of O2 recombines.
How ozone from air ionizers is hazardous to human health?
Ozone is potentially a harmful gas that produces more chronic respiratory diseases and disorders. When exposed to high levels of ozone, it might end up lethal by damaging the lungs and the olfactory bulb and reduce the sense of odor. Ozone being highly reactive, they react with the inner walls of the lungs to facilitate a type of heart disease called Atherosclerosis. Though this disease is often related with the Ozone that is created in our body, the ozone when inhaled would be lethal too.
Low Concentrations of Ozone are lethal too
Several safety board emphasizes that the ozone, even when it is produced within the safety standards, is not desirable for humans, due to their high reactive nature. They are capable of forming chemical compounds that would turn toxic too. As the regulatory boards have no control over the ozone generation in the air ionizers, they are out of options to prevent the users from ozone exposure. This low concentration exposure is potentially dangerous for people who spend most of their time indoors next to the air ionizer, as the half-life of O3 at normal room temperature is around three days.
Though negative ions help in purifying your air around, according to some controlled studies of the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), the ozone levels could go beyond the safety standard even when a consumer follows the instruction manual of an air ionizer.
The purifier placement also increases the risk. The closer you get to the purifier, the stronger the concentration of the ozone will be. Imagine an air ionizer next to your table, right above your head while you sleep or just a few inches away from you, when you drive.
These potential risks of air ionizers are denied by the companies that manufacture them, as they still prefer their business to the safety of humans.
This post was first published on March 20, 2014.